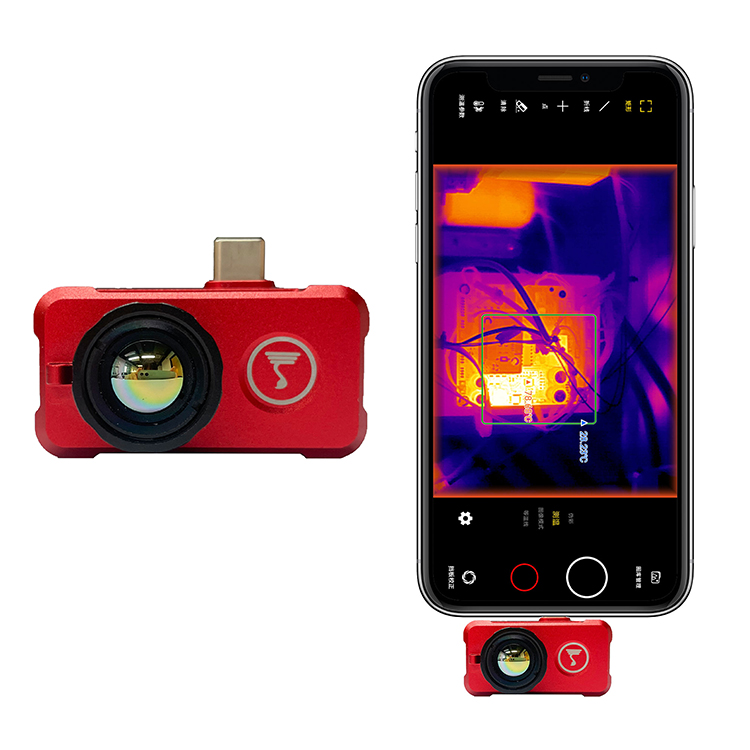
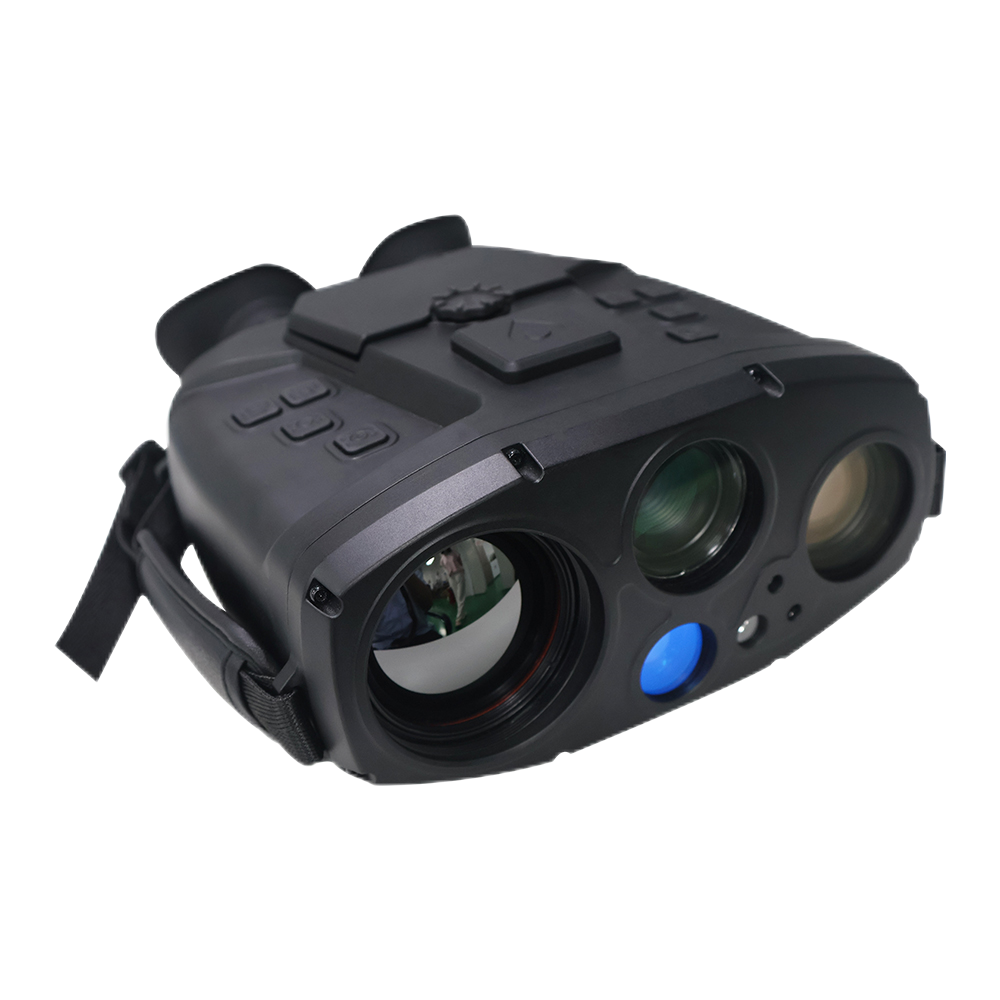
Thermal imaging principle
2024年8月21日Infrared Thermal Imaging Paves the Way for New Driving Frontiers
2024年9月24日In the “reconnaissance-strike” kill chain, the application of sensor night vision technology can greatly enhance the situational awareness of the all-weather battlefield and create tactical advantages. Which one is the “fire eye” in night combat, low-light enhancement or thermal imager? Why has thermal imaging technology, which was once only used in high-end applications such as military, flooded into the civilian market?
- The “third eye” of night battles
From ancient times to the present, battles have often been fought at night. Using night vision technologies such as low-light enhancement and infrared thermal imaging, combat troops can break through the barriers of the night and gain the freedom of night battles. After soldiers, tanks, ships, aircraft and other equipment are equipped with night vision equipment, the effective combat time is greatly extended.
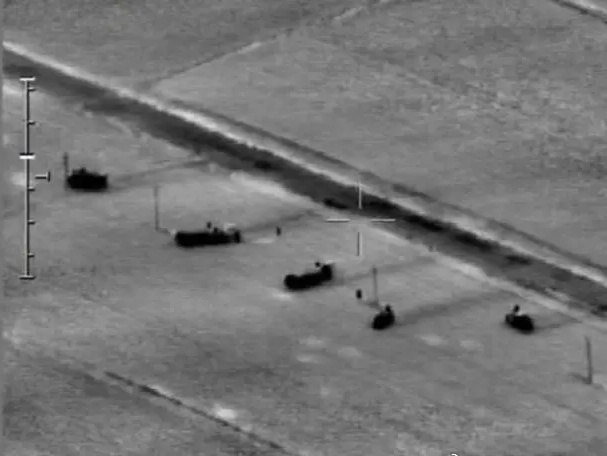

Ground armored vehicles under night vision goggles
1) Low-light enhancement and amplification
Low-light night vision devices have become the most widely used type of night vision devices by the military of various countries because of their simple principle, good image quality and low cost. They are basically based on the third and fourth generation tube low-light night vision technology, such as the mainstream night vision devices AN/PVS-31 and GPNVG-18 of the US special forces that use the third generation film-free white phosphorus enhancement tube; the LUCIE night vision devices equipped by the French, German and other European armies are all low-light night vision devices.
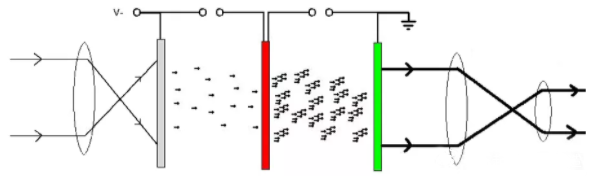
Schematic diagram of the structure and principle of low-light night vision device
Low-light-level night vision devices are also known as image enhancement technology, which is actually to enhance and amplify the tiny electronic signal of the light source to make it visible. In an extremely low-light environment, the image intensifier can be used to illuminate the object with weak light such as moonlight and starlight or infrared detection light. The light reflected by the object is amplified by the image intensifier and converted into an image that can be clearly observed by the human eye, thereby realizing the observation of the target at night. Therefore, the image intensifier tube is a key component of the low-light-level night vision device, and its quality directly determines the effect of the night vision device.
Low-light night vision goggles are certainly useful, but they are not very effective when used on cloudy days, in pitch-black conditions, or in smoky conditions. This is when more advanced infrared thermal imaging night vision goggles come in handy.
2) Ubiquitous infrared thermal radiation
Light is an electromagnetic wave. Our naked eyes can only see the world between 400-600nm in the electromagnetic wave. Humans lack the visual ability to perceive temperature. The invisible light with a wavelength between 760-1000nm is called infrared (IR). In our lives, whether it is biological or mechanical, even ice, it will emit heat energy, and the wavelength of thermal radiation is in the infrared band.
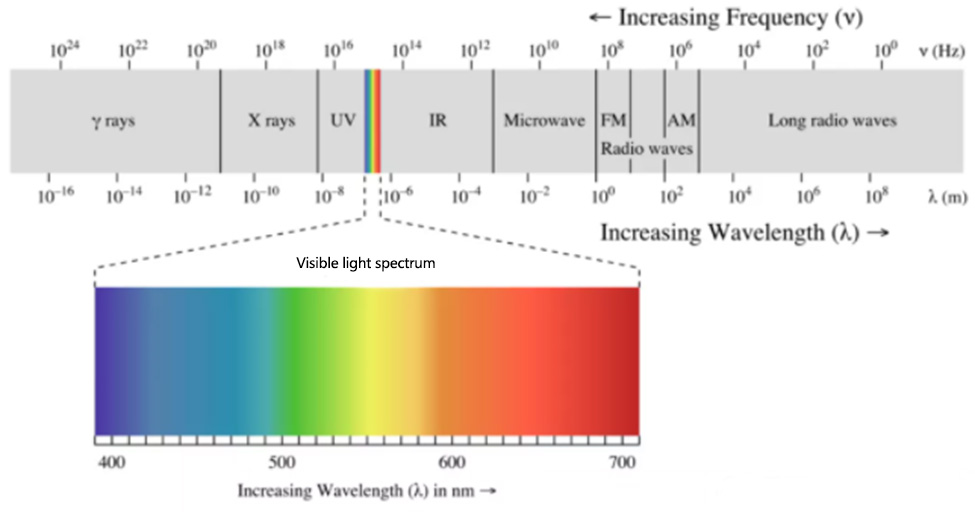
Electromagnetic spectrum
Similar to cameras that image visible light, thermal imagers are devices that image infrared light by passively receiving radiation from the target without actively sending out signals. Due to the different intensities of infrared light radiated by different objects, the thermal imager is first used to obtain the target’s thermal radiation information, and then the target object is identified based on the difference in infrared light radiated by the target object and the background object.
The real advantage of thermal imaging lies in target observation and recognition. As long as the surface emissivity of the target is different from that of the background, or as long as the target has its own temperature, thermal imaging can easily distinguish the target through the temperature difference. For example, in the woods, although thermal imaging can only see the treetops that are blurred together, it can easily see all the animals within a range of more than 100 meters. Even if they are covered by grass or other things, as long as there is a little shadow, the user can find them, which is difficult to do with infrared and low light.
3) Super CP-composite night vision solution
Of course, thermal imagers are not omnipotent. Since they rely on temperature difference imaging, the image contrast is low, and the target cannot be seen clearly through obstacles such as glass.
Thermal imaging also has its own disadvantages compared to infrared micro-light. Thermal imaging relies on the surface temperature of the target to distinguish the target, and the surface temperature is affected by the surface material of the object, and the emissivity varies greatly. If a large number of objects with very small surface temperature differences are piled up in the picture, thermal imaging is difficult to distinguish, which will cause the picture to become a mess. For example, it is usually difficult to distinguish the details of the ground grass and tree canopy with thermal imaging. If you only rely on thermal imaging to act at night, it is easy to fail on rugged ground.
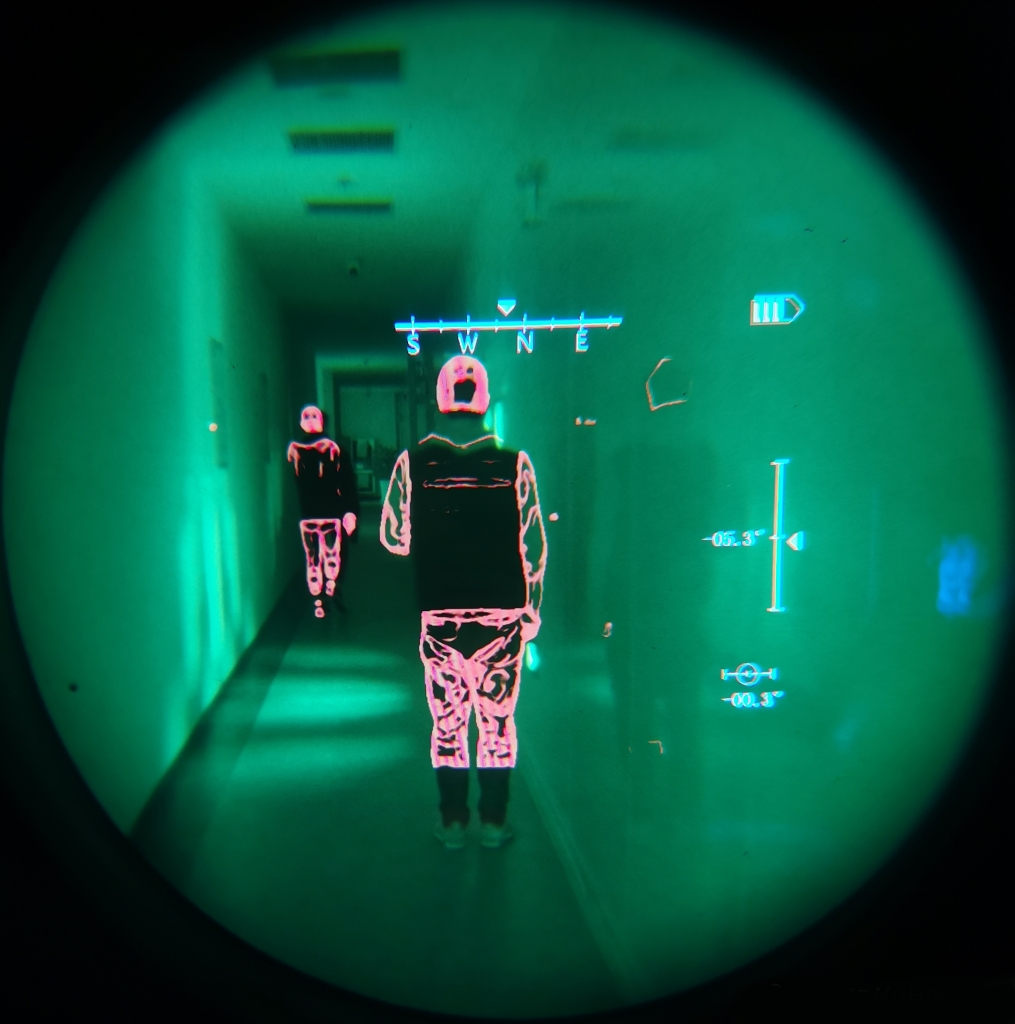

Fusion contour imaging effect of enhanced night vision goggles
So the composite night vision device that integrates low-light night vision goggles and infrared thermal imaging came on the scene. Taking the fourth-generation AN/PVS-21 binocular night vision device of the United States as an example, its dual lenses give it two optical channels, which can superimpose the infrared imaging and low-light imaging of the target after processing. Even in a completely dark environment, it can see the infrared image of the heat source emitted by the enemy through the camouflage.
- Driving the future of all-weather autonomous driving
As the technological high ground of the next stage, thermal imagers will also play an important driving role in the development of future autonomous driving. Many companies are trying to obtain true autonomous driving technology and redefine cars by exploring different solutions.

Car infrared night vision cameras can help drivers perceive the road environment
At present, the mainstream of autonomous driving technology is lidar and visual sensor perception solutions. The basic idea is to use different sensors to “fill in the gaps” with each other to achieve better overall results. However, at night or in extreme weather conditions, both sensors have certain physical limitations, which indirectly leads to the inability of autonomous driving technology to be used in corresponding scenarios.
In a broad sense, fully autonomous driving requires all-weather driving capabilities – which means that the vehicle needs to have situational awareness capabilities beyond humans, which is inseparable from the information input by the thermal imaging modality in various scenarios.
Some mainstream autonomous driving research institutions have confirmed that due to the introduction of thermal radiation information of objects, the thermal imaging system installed on the car can detect objects that visual sensors and lidar cannot recognize, and can efficiently and stably identify objects such as pedestrians and vehicles, and better integrate with the radar mode.
In essence, it abandons the color information of objects that has little effect on autonomous driving and focuses on the texture information of objects. The introduction of thermal imaging mode can fundamentally improve the system’s detection capabilities at night and in rainy and foggy conditions, and give the system more information redundancy to reduce accidents.












